7.5 KiB
Example 2
This example aims to provide instructions on how to filter scan messages.
For robots with laser scanners, ROS provides a special Message type in the sensor_msgs package called LaserScan to hold information about a given scan. Let's take a look at the message specifications:
# Laser scans angles are measured counter clockwise, with Stretch's LiDAR having
# both angle_min and angle_max facing forward (very closely along the x-axis)
Header header
float32 angle_min # start angle of the scan [rad]
float32 angle_max # end angle of the scan [rad]
float32 angle_increment # angular distance between measurements [rad]
float32 time_increment # time between measurements [seconds]
float32 scan_time # time between scans [seconds]
float32 range_min # minimum range value [m]
float32 range_max # maximum range value [m]
float32[] ranges # range data [m] (Note: values < range_min or > range_max should be discarded)
float32[] intensities # intensity data [device-specific units]
The above message tells you everything you need to know about a scan. Most importantly, you have the angle of each hit and its distance (range) from the scanner. If you want to work with raw range data, then the above message is all you need. There is also an image below that illustrates the components of the message type.
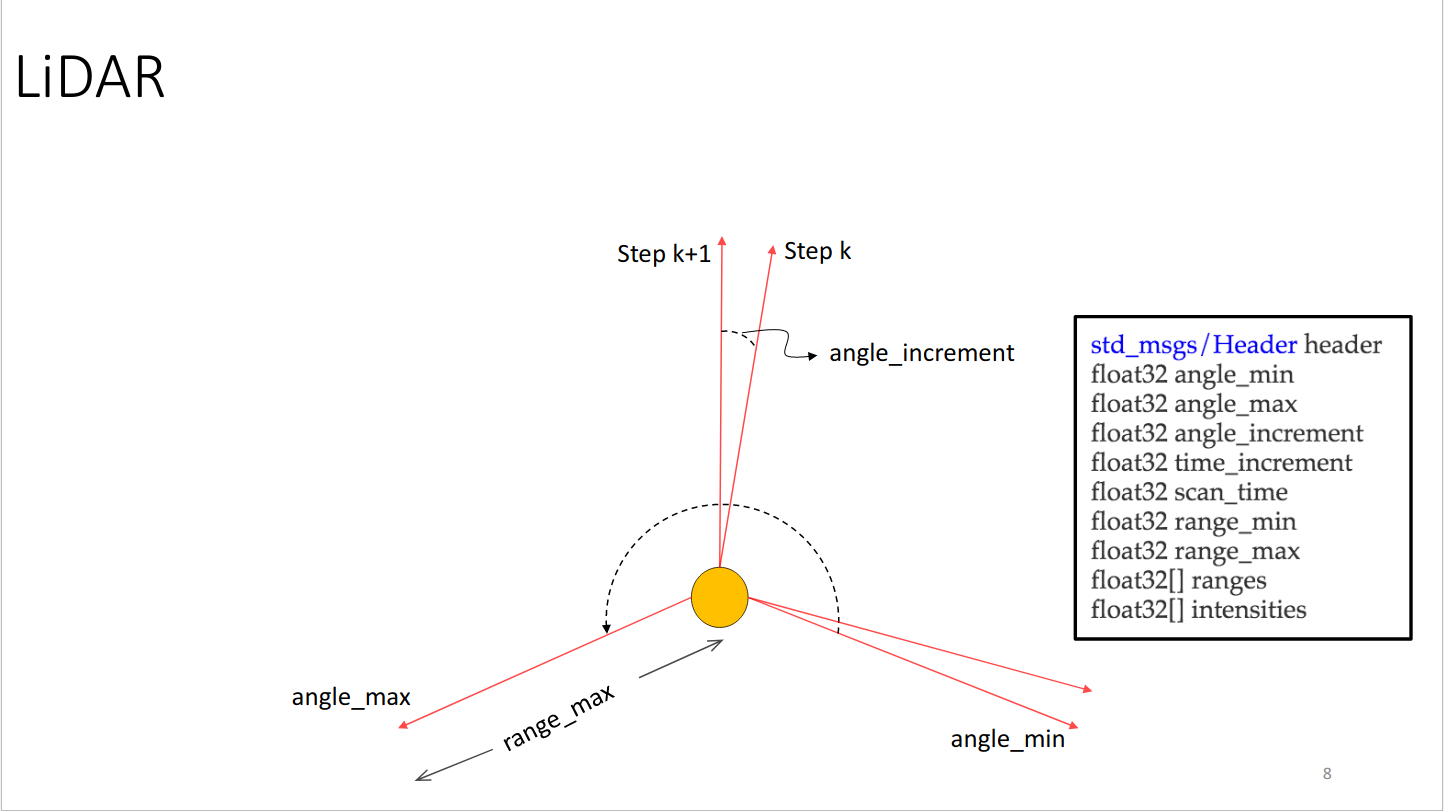
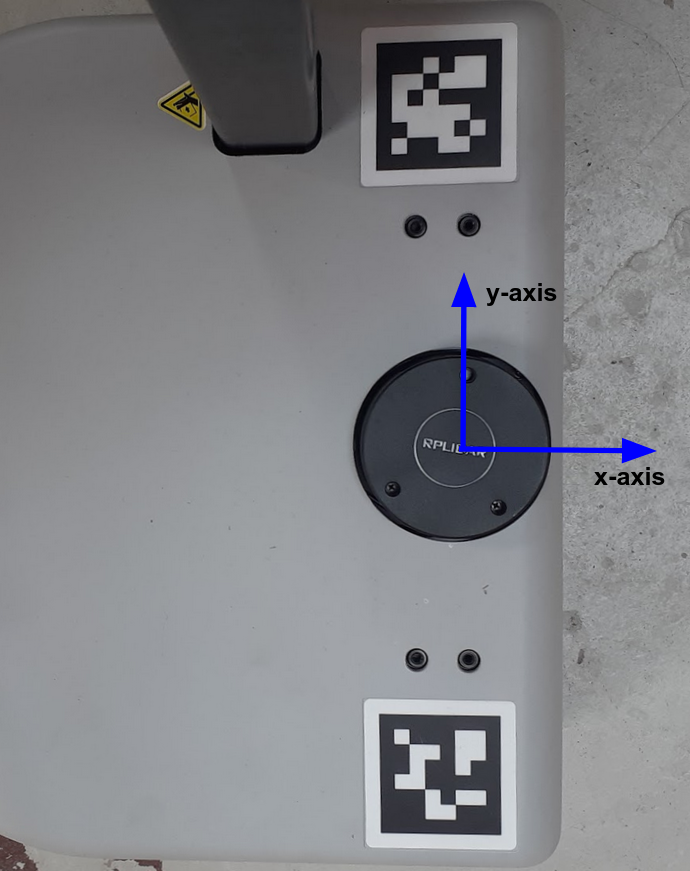
For a Stretch robot the start angle of the scan, angle_min, and
end angle, angle_max, are closely located along the x-axis of Stretch's frame. angle_min and angle_max are set at -3.1416 and 3.1416, respectively. This is illustrated by the images below.
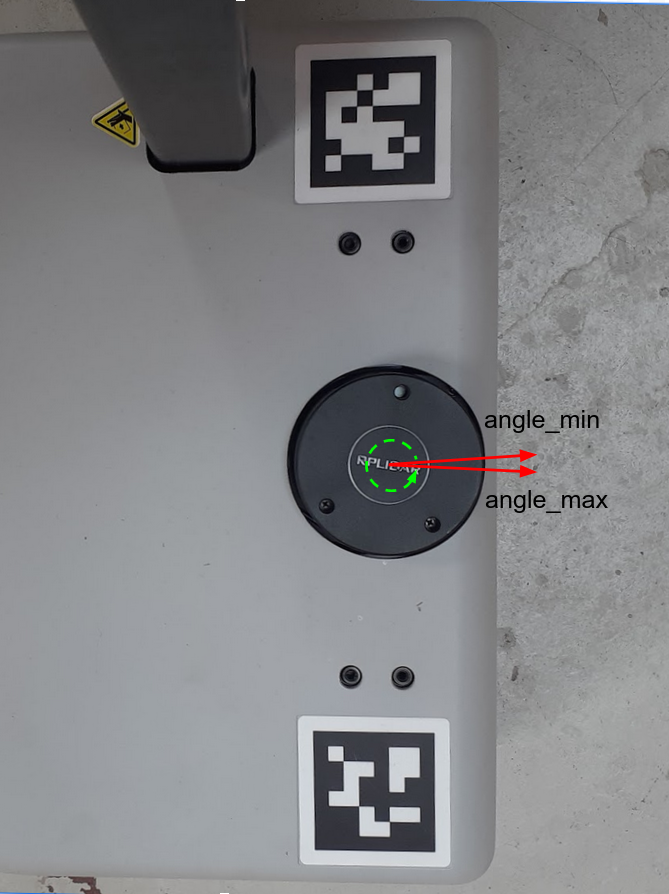


Knowing the orientation of the LiDAR allows us to filter the scan values for a desired range. In this case, we are only considering the scan ranges in front of the stretch robot.
First, open a terminal and run the stretch driver launch file.
roslaunch stretch_core stretch_driver.launch
Then in a new terminal run the rplidar.launch file from stretch_core.
roslaunch stretch_core rplidar.launch
To filter the lidar scans for ranges that are directly in front of Stretch (width of 1 meter) run the scan_filter.py node by typing the following in a new terminal.
cd catkin_ws/src/stretch_tutorials/src/
python3 scan_filter.py
Then run the following command in a separate terminal to bring up a simple RViz configuration of the Stretch robot.
rosrun rviz rviz -d `rospack find stretch_core`/rviz/stretch_simple_test.rviz
Change the topic name from the LaserScan display from /scan to /filter_scan.
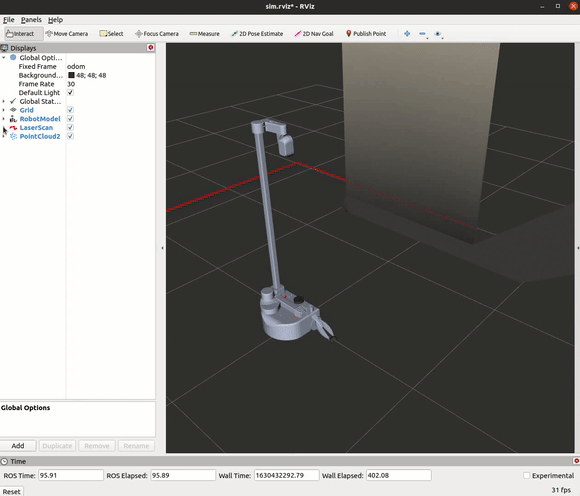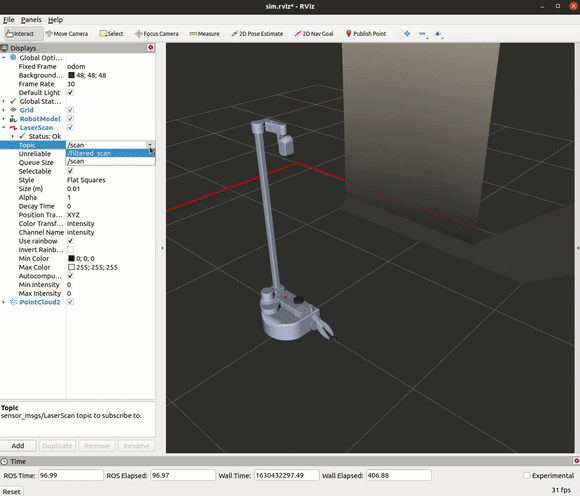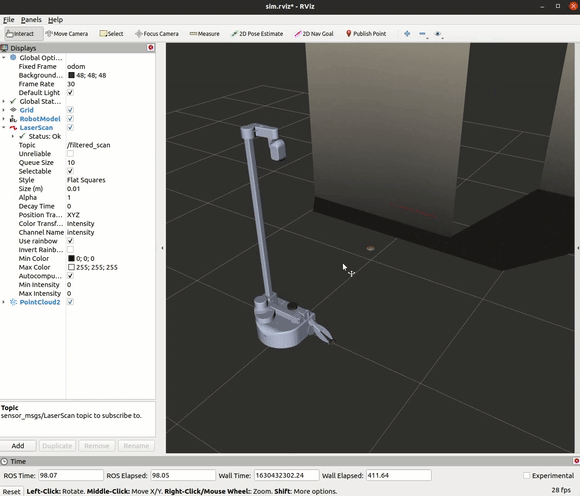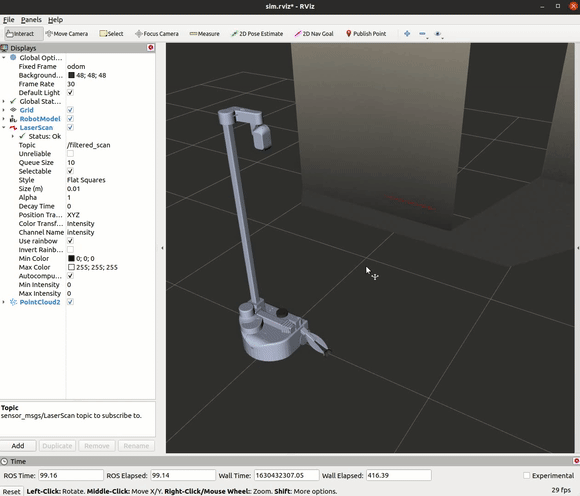
The Code
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import rospy
from numpy import linspace, inf
from math import sin
from sensor_msgs.msg import LaserScan
class ScanFilter:
"""
A class that implements a LaserScan filter that removes all of the points
that are not in front of the robot.
"""
def __init__(self):
self.width = 1.0
self.extent = self.width / 2.0
self.sub = rospy.Subscriber('/scan', LaserScan, self.callback)
self.pub = rospy.Publisher('filtered_scan', LaserScan, queue_size=10)
rospy.loginfo("Publishing the filtered_scan topic. Use RViz to visualize.")
def callback(self,msg):
"""
Callback function to deal with incoming LaserScan messages.
:param self: The self reference.
:param msg: The subscribed LaserScan message.
:publishes msg: updated LaserScan message.
"""
angles = linspace(msg.angle_min, msg.angle_max, len(msg.ranges))
points = [r * sin(theta) if (theta < -2.5 or theta > 2.5) else inf for r,theta in zip(msg.ranges, angles)]
new_ranges = [r if abs(y) < self.extent else inf for r,y in zip(msg.ranges, points)]
msg.ranges = new_ranges
self.pub.publish(msg)
if __name__ == '__main__':
rospy.init_node('scan_filter')
ScanFilter()
rospy.spin()
The Code Explained
Now let's break the code down.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
Every Python ROS Node will have this declaration at the top. The first line makes sure your script is executed as a Python3 script.
import rospy
from numpy import linspace, inf
from math import sin
from sensor_msgs.msg import LaserScan
You need to import rospy if you are writing a ROS Node. There are functions from numpy and math that are required within this code, that's why linspace, inf, and sin are imported. The sensor_msgs.msg import is so that we can subscribe and publish LaserScan messages.
self.width = 1
self.extent = self.width / 2.0
We're going to assume that the robot is pointing up the x-axis so that any points with y coordinates further than half of the defined width (1 meter) from the axis are not considered.
self.sub = rospy.Subscriber('/scan', LaserScan, self.callback)
Set up a subscriber. We're going to subscribe to the topic scan, looking for LaserScan messages. When a message comes in, ROS is going to pass it to the function callback automatically.
self.pub = rospy.Publisher('filtered_scan', LaserScan, queue_size=10)
pub = rospy.Publisher("filtered_scan", LaserScan, queue_size=10) declares that your node is publishing to the filtered_scan topic using the message type LaserScan. This lets the master tell any nodes listening on filtered_scan that we are going to publish data on that topic.
angles = linspace(msg.angle_min, msg.angle_max, len(msg.ranges))
This line of code utilizes linspace to compute each angle of the subscribed scan.
points = [r * sin(theta) if (theta < -2.5 or theta > 2.5) else inf for r,theta in zip(msg.ranges, angles)]
Here we are computing the y coordinates of the ranges that are below -2.5 and above 2.5 radians of the scan angles. These limits are sufficient for considering scan ranges in front of Stretch, but these values can be altered to your preference.
new_ranges = [r if abs(y) < self.extent else inf for r,y in zip(msg.ranges, points)]
If the absolute value of a point's y-coordinate is under self.extent then keep the range, otherwise use inf, which means "no return".
msg.ranges = new_ranges
self.pub.publish(msg)
Substitute the new ranges in the original message, and republish it.
rospy.init_node('scan_filter')
ScanFilter()
The next line, rospy.init_node(NAME, ...), is very important as it tells rospy the name of your node -- until rospy has this information, it cannot start communicating with the ROS Master.
!!! note The name must be a base name, i.e. it cannot contain any slashes "/".
Instantiate the class with ScanFilter()
rospy.spin()
Give control to ROS. This will allow the callback to be called whenever new messages come in. If we don't put this line in, then the node will not work, and ROS will not process any messages.
