5.7 KiB
Intro to Navigation
Display
Visualize the robot in Rviz:
roslaunch stretch_core stretch.launch lidar_odom:=false respeaker:=false rviz:=true
For more details on the arguments, see the API docs.
Simulation
Visualize the simulated robot in Rviz:
roslaunch stretch_gazebo gazebo.launch rviz:=true
Untethered Operation
At this point, we want to remove all wires tethered Stretch to our monitor/keyboard/etc. We'll set up "ROS Remote Master", which is a feature built into ROS that allows untethered operation. Follow this guide: https://docs.hello-robot.com/0.2/stretch-tutorials/getting_started/untethered_operation/#ros-remote-master
# on the robot
roslaunch stretch_core stretch.launch lidar_odom:=false respeaker:=false
# on your personal computer
rviz -d `rospack find stretch_core`/rviz/stretch.rviz
Teleoperation
Switch to 'navigation' mode:
rosservice call /switch_to_navigation_mode
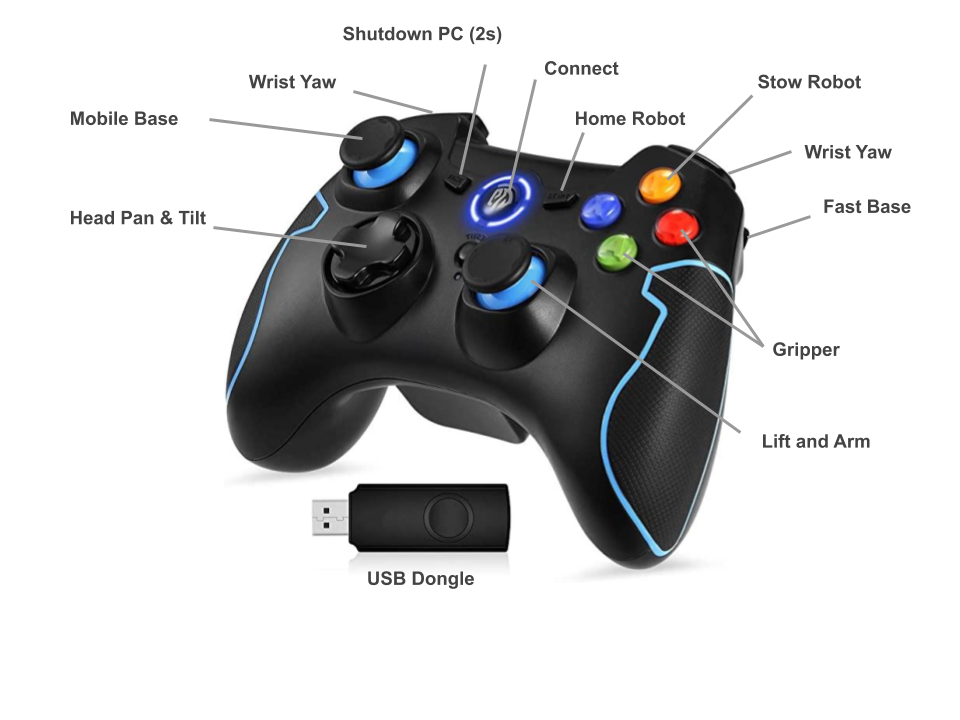
On your personal computer, plug in the controller dongle and run base keyboard teleop:
roslaunch stretch_core teleop_twist.launch
or if you have the Xbox controller:
roslaunch stretch_core teleop_twist.launch teleop_type:=joystick
The deadman button is the 'A' button (the green one).
/stretch/cmd_vel
The /stretch/cmd_vel topic accepts Twist msgs, where twist.linear.x and twist.angular.z are the translational and angular velocities the mobile base will execute.
$ rostopic echo /stretch/cmd_vel
---
linear:
x: -0.04
y: 0.0
z: 0.0
angular:
x: 0.0
y: 0.0
z: -0.05731585025787354
---
linear:
x: 0.0
y: 0.0
z: 0.0
angular:
x: 0.0
y: 0.0
z: 0.0
---
Safety
Velocity commands must be sent at a regular control rate and must be faster than 2hz. There's two safety behaviors that prevent a runaway robot. A software check smoothly stops base motion after 0.5 seconds if no new command is received. A hardware check abruptly stops base motion after 1 second if no new command is received.
Mapping (slides)
Stop all previous ROS commands. Start the following ROS commands on your Stretch.
Start the mapping launch file:
roslaunch stretch_navigation mapping.launch rviz:=false teleop_type:=none
Turn on the robot's head camera as well:
roslaunch stretch_core stretch_realsense.launch publish_upright_img:=true
Use keyboard teleop to tilt the head camera downwards to look at the floor in front of the robot:
rosrun stretch_core keyboard_teleop
Now, on your computer, launch Rviz:
rviz -d `rospack find stretch_navigation`/rviz/mapping.rviz
Start controller teleop:
roslaunch stretch_core teleop_twist.launch teleop_type:=joystick linear:=0.12 angular:=0.3
After moving around the environment for some time, you can save the map using:
rosrun map_server map_saver -f ${HELLO_FLEET_PATH}/maps/oct24thmap
Planning
Stop all previous ROS commands. Start the following ROS commands on your Stretch.
roslaunch stretch_navigation navigation.launch map_yaml:=${HELLO_FLEET_PATH}/maps/oct24thmap.yaml rviz:=false
Start Rviz on your personal computer:
rviz -d `rospack find stretch_navigation`/rviz/navigation.rviz
Localization
AMCL is very commonly used for localization. It's a particle filtering library that works by comparing the robot's motion and sensor updates with a distribution of guesses at the robot's position in order to eliminate unlikely guesses every iteration. Running these motion/sensor update steps will allow the filter to converge on the robot's position as the robot sees landmarks. When the robot "wakes up", it doesn't know where it is, and the particles are evenly distributed across the map. We tell the robot where it is using:
- The position estimate GUI in Rviz
- Detecting a unique landmark (e.g. a Aruco marker taped to the wall)
- Spinning in a 360 degree circle
For example, turn on particle filters visualization in Rviz, use the Pose Estimate GUI to put the robot off somewhere wrong, and run teleop:
roslaunch stretch_core teleop_twist.launch teleop_type:=joystick linear:=0.12 angular:=0.3
Now spin the robot in a 360 degree circle. This doesn't always work, especially in environments with repetitive features.
Costmaps (slides)
Global Plan (slides)
The global planner is called navfn/NavfnROS
To visualize the global plan without moving the robot, switch the robot into position mode:
rosservice call /switch_to_position_mode
Use the Nav Goal GUI to send goals to MoveBase and visualize the global plans.
Now cancel the plan:
rostopic pub /move_base/cancel actionlib_msgs/GoalID "stamp:
secs: 0
nsecs: 0
id: ''"
Plan Follower
The local planner is called TrajectoryPlannerROS
Code Examples
- https://docs.hello-robot.com/0.2/stretch-tutorials/ros1/example_13/
- https://docs.hello-robot.com/0.2/stretch-tutorials/ros1/autodocking_nav_stack/