9.8 KiB
Capture Image
Example 7
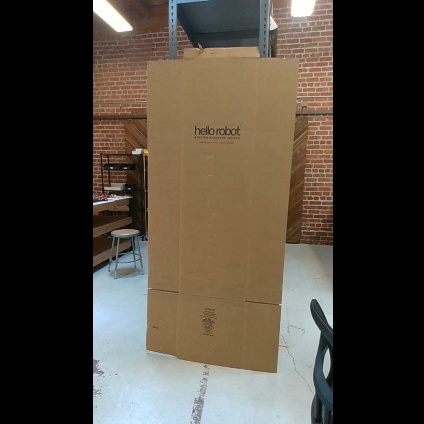
In this example, we will review a Python script that captures an image from the RealSense camera.

Begin by running the stretch driver.launch file.
ros2 launch stretch_core stretch_driver.launch.py
To activate the RealSense camera and publish topics to be visualized, run the following launch file in a new terminal.
ros2 launch stretch_core d435i_low_resolution.launch.py
Within this tutorial package, there is an RViz config file with the topics for perception already in the Display tree. You can visualize these topics and the robot model by running the command below in a new terminal.
ros2 run rviz2 rviz2 -d /home/hello-robot/ament_ws/src/stretch_tutorials/rviz/perception_example.rviz
Capture Image with Python Script
In this section, we will use a Python node to capture an image from the RealSense camera. Execute the capture_image.py node to save a .jpeg image of the image topic /camera/color/image_raw. In a terminal, execute:
cd ~/ament_ws/src/stretch_tutorials/stretch_ros_tutorials
python3 capture_image.py
An image named camera_image.jpeg is saved in the stored_data folder in this package, if you don't have this folder you can create it yourself.
The Code
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import rclpy
import sys
import os
import cv2
from rclpy.node import Node
from sensor_msgs.msg import Image
from cv_bridge import CvBridge, CvBridgeError
class CaptureImage(Node):
"""
A class that converts a subscribed ROS image to a OpenCV image and saves
the captured image to a predefined directory.
"""
def __init__(self):
"""
A function that initializes a CvBridge class, subscriber, and save path.
:param self: The self reference.
"""
super().__init__('stretch_capture_image')
self.bridge = CvBridge()
self.sub = self.create_subscription(Image, '/camera/color/image_raw', self.image_callback, 10)
self.save_path = '/home/hello-robot/ament_ws/src/stretch_tutorials/stored_data'
self.br = CvBridge()
def image_callback(self, msg):
"""
A callback function that converts the ROS image to a CV2 image and stores the
image.
:param self: The self reference.
:param msg: The ROS image message type.
"""
try:
image = self.bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(msg, 'bgr8')
except CvBridgeError as e:
self.get_logger().warn('CV Bridge error: {0}'.format(e))
file_name = 'camera_image.jpeg'
completeName = os.path.join(self.save_path, file_name)
cv2.imwrite(completeName, image)
rclpy.shutdown()
sys.exit(0)
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
capture_image = CaptureImage()
rclpy.spin(capture_image)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
The Code Explained
Now let's break the code down.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
Every Python ROS Node will have this declaration at the top. The first line makes sure your script is executed as a Python3 script.
import rclpy
import sys
import os
import cv2
You need to import rclpy if you are writing a ROS Node. There are functions from sys, os, and cv2 that are required within this code. cv2 is a library of Python functions that implements computer vision algorithms. Further information about cv2 can be found here: OpenCV Python.
from rclpy.node import Node
from sensor_msgs.msg import Image
from cv_bridge import CvBridge, CvBridgeError
The sensor_msgs.msg is imported so that we can subscribe to ROS Image messages. Import CvBridge to convert between ROS Image messages and OpenCV images and the Node is neccesary to create a node in ROS2.
def __init__(self):
"""
A function that initializes a CvBridge class, subscriber, and save path.
:param self: The self reference.
"""
super().__init__('stretch_capture_image')
self.bridge = CvBridge()
self.sub = self.create_subscription(Image, '/camera/color/image_raw', self.image_callback, 10)
self.save_path = '/home/hello-robot/ament_ws/src/stretch_tutorials/stored_data'
self.br = CvBridge()
Initialize the node, CvBridge class, the subscriber, and the directory where the captured image will be stored.
def image_callback(self, msg):
"""
A callback function that converts the ROS image to a cv2 image and stores the
image.
:param self: The self reference.
:param msg: The ROS image message type.
"""
try:
image = self.bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(msg, 'bgr8')
except CvBridgeError as e:
rospy.logwarn('CV Bridge error: {0}'.format(e))
Try to convert the ROS Image message to a cv2 Image message using the imgmsg_to_cv2() function.
file_name = 'camera_image.jpeg'
completeName = os.path.join(self.save_path, file_name)
cv2.imwrite(completeName, image)
Join the directory and file name using the path.join() function. Then use the imwrite() function to save the image.
rclpy.shutdown()
sys.exit(0)
The first line of code initiates a clean shutdown of ROS. The second line of code exits the Python interpreter.
rclpy.init(args=args)
capture_image = CaptureImage()
The next line, rclpy.init_node initializes the node. In this case, your node will take on the name 'stretch_capture_image'. Also setup CaptureImage class with capture_image = CaptureImage().
!!! note The name must be a base name, i.e. it cannot contain any slashes "/".
rclpy.spin(capture_image)
Give control to ROS. This will allow the callback to be called whenever new messages come in. If we don't put this line in, then the node will not work, and ROS will not process any messages.
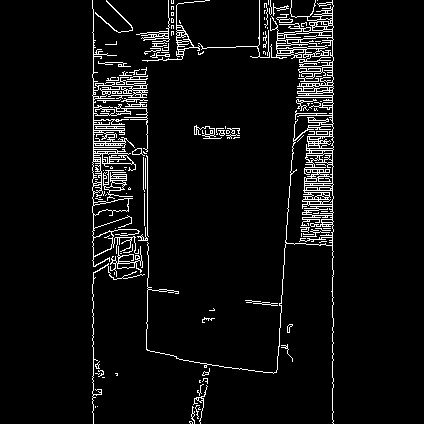
Edge Detection
In this section, we highlight a node that utilizes the Canny Edge filter algorithm to detect the edges from an image and convert it back as a ROS image to be visualized in RViz. In a terminal, execute:
cd ~/ament_ws/src/stretch_tutorials/stretch_ros_tutorials
python3 edge_detection.py
The node will publish a new Image topic named /image_edge_detection. This can be visualized in RViz and a gif is provided below for reference.
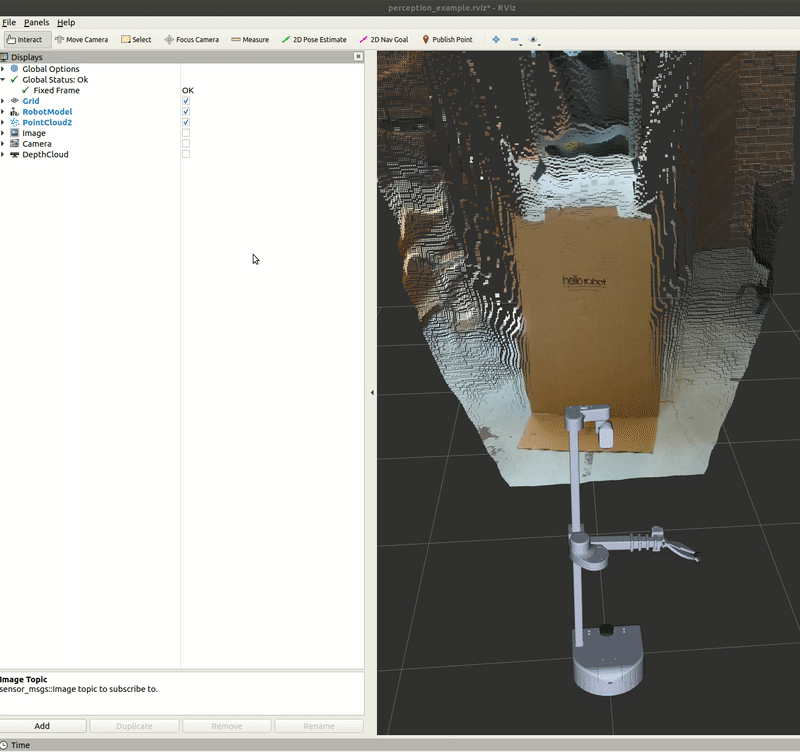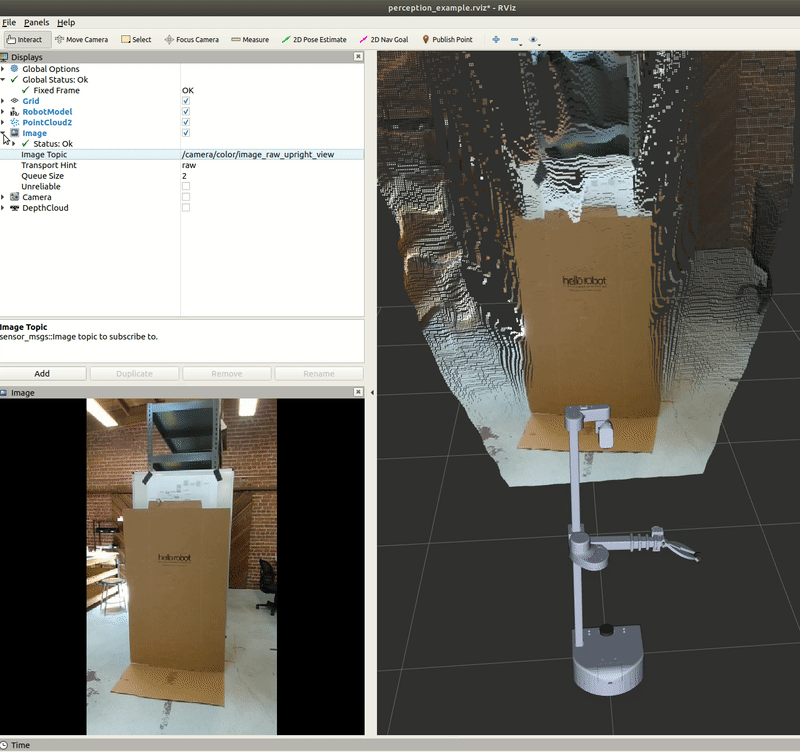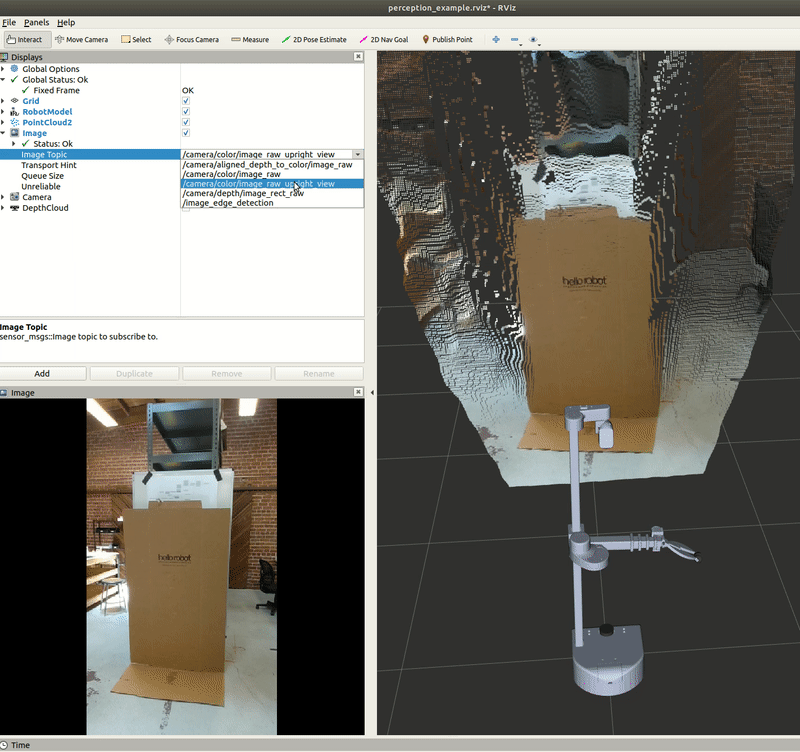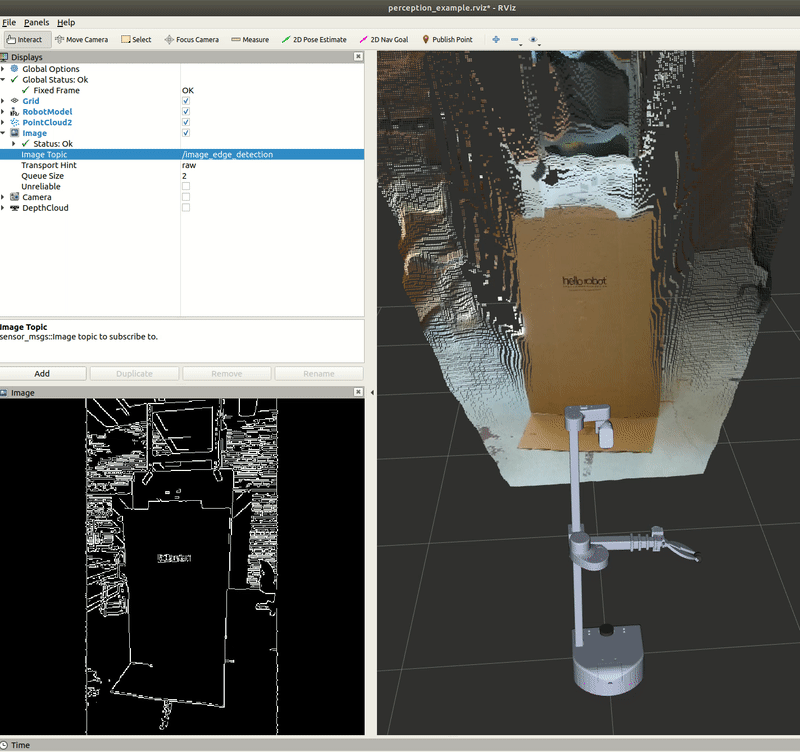
The Code
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
import cv2
from sensor_msgs.msg import Image
from cv_bridge import CvBridge, CvBridgeError
class EdgeDetection(Node):
"""
A class that converts a subscribed ROS image to a OpenCV image and saves
the captured image to a predefined directory.
"""
def __init__(self):
"""
A function that initializes a CvBridge class, subscriber, and other
parameter values.
:param self: The self reference.
"""
super().__init__('stretch_edge_detection')
self.bridge = CvBridge()
self.sub = self.create_subscription(Image, '/camera/color/image_raw', self.callback, 1)
self.pub = self.create_publisher(Image, '/image_edge_detection', 1)
self.save_path = '/home/hello-robot/catkin_ws/src/stretch_tutorials/stored_data'
self.lower_thres = 100
self.upper_thres = 200
self.get_logger().info("Publishing the CV2 Image. Use RViz to visualize.")
def callback(self, msg):
"""
A callback function that converts the ROS image to a CV2 image and goes
through the Canny Edge filter in OpenCV for edge detection. Then publishes
that filtered image to be visualized in RViz.
:param self: The self reference.
:param msg: The ROS image message type.
"""
try:
image = self.bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(msg, 'bgr8')
except CvBridgeError as e:
self.get_logger().warn('CV Bridge error: {0}'.format(e))
image = cv2.Canny(image, self.lower_thres, self.upper_thres)
image_msg = self.bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg(image, 'passthrough')
image_msg.header = msg.header
self.pub.publish(image_msg)
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
edge_detection = EdgeDetection()
rclpy.spin(edge_detection)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
The Code Explained
Since there are similarities in the capture image node, we will only break down the different components of the edge detection node.
Define the lower and upper bounds of the Hysteresis Thresholds.
image = cv2.Canny(image, self.lower_thres, self.upper_thres)
Run the Canny Edge function to detect edges from the cv2 image.
image_msg = self.bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg(image, 'passthrough')
Convert the cv2 image back to a ROS image so it can be published.
image_msg.header = msg.header
self.pub.publish(image_msg)
Publish the ROS image with the same header as the subscribed ROS message.
